What is WebDAV Protocol?
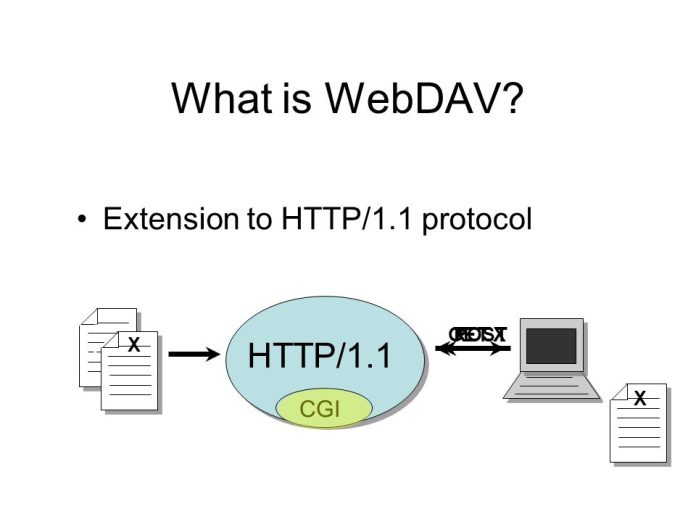
WebDAV, which stands for Web Distributed Authoring and Versioning, is an extension of the Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) that facilitates collaborative editing and managing of files stored on web servers. It allows users to remotely manage files on web servers, enabling functionalities like file creation, modification, and deletion directly on the server.
Understanding the Basics of WebDAV
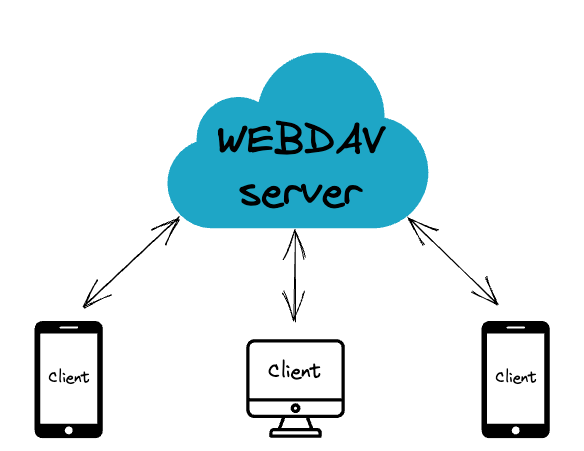
WebDAV operates on the client-server model, where clients interact with remote servers using HTTP or HTTPS protocols. It extends the capabilities of HTTP to support collaborative editing and file management over the internet. Read about Which VPNS Do Hackers Use
History and Evolution of
WebDAV was first introduced in 1996 by a group of engineers at the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C). It was designed to address the limitations of traditional file transfer protocols by providing a standardized method for remote file management.
Key Features and Benefits of WebDAV
WebDAV offers several key features and benefits, including:
- File Locking: Users can lock files to prevent concurrent editing and maintain data integrity.
- Versioning: WebDAV supports versioning, allowing users to track changes and revert to previous versions of files.
- Properties: It enables the storage of metadata associated with files, such as authorship and creation date.
- Namespace Manipulation: Users can create, move, copy, and delete files and directories on the server.
How WebDAV Works
WebDAV operates by extending the HTTP protocol with additional methods and headers to support file management operations. Clients communicate with WebDAV-enabled servers using standard HTTP requests, such as GET, PUT, POST, DELETE, and PROPFIND.
Common Use Cases of WebDAV
WebDAV is commonly used in various scenarios, including:
- Collaborative document editing and sharing
- Content management systems (CMS)
- Remote backup and synchronization
- Web application development and deployment
Implementing WebDAV in Different Environments
WebDAV can be implemented on a wide range of platforms and operating systems, including Windows, macOS, Linux, and mobile devices. Many web servers and cloud storage providers offer built-in support for WebDAV. Don’t Miss to Check Out Our Website: Globall Browse
Security Considerations with WebDAV
Security is a critical aspect of WebDAV implementation. It is essential to use secure communication channels (HTTPS) and enforce access controls to protect sensitive data from unauthorized access and manipulation.
Comparison with Other Protocols
WebDAV offers several advantages over traditional file transfer protocols like FTP and SCP, including improved interoperability, support for metadata, and robust versioning capabilities.
Challenges and Limitations of WebDAV
Despite its advantages, WebDAV also has some limitations, such as compatibility issues with certain client applications and performance overhead associated with file locking and versioning.
Future Trends and Developments in WebDAV
The future of WebDAV is likely to focus on improving performance, enhancing security, and expanding compatibility with emerging technologies and protocols.
Tips for Using WebDAV Effectively
To make the most of WebDAV, consider the following tips:
- Choose a reliable WebDAV client with support for essential features and security standards.
- Regularly backup files and monitor server logs for suspicious activity.
- Stay informed about updates and patches to address security vulnerabilities and compatibility issues.

Best Practices for WebDAV Implementation
When implementing WebDAV, adhere to best practices such as:
- Enforce strong authentication and access controls to prevent unauthorized access.
- Implement encryption to protect data in transit and at rest.
- Regularly audit file permissions and review server configurations for security gaps.
Conclusion
In conclusion, WebDAV is a powerful protocol that enables collaborative file management and versioning over the web. By understanding its features, benefits, and implementation considerations, organizations can leverage WebDAV to streamline workflows, improve productivity, and enhance data security.
FAQs
- Is WebDAV secure for transferring sensitive data?
- WebDAV can be secure if implemented correctly with proper encryption and access controls. However, it is essential to follow security best practices to mitigate potential risks.
- Can WebDAV be integrated with existing content management systems (CMS)? Yes, many CMS platforms support WebDAV integration, allowing users to manage files and content remotely.
- What are the main advantages of using WebDAV over traditional file transfer protocols?
- WebDAV offers advantages such as improved interoperability, support for metadata, and robust versioning capabilities, which are not typically available in traditional protocols like FTP.
- Are there any limitations to using WebDAV?
- While WebDAV offers numerous benefits, it may encounter compatibility issues with certain client applications and impose performance overhead due to file locking and versioning mechanisms.
- What are some alternative protocols to WebDAV for remote file management? Alternatives to WebDAV include FTP, SCP, and cloud-based file storage solutions. However, each protocol has its own strengths and limitations, so it is essential to choose the one that best suits your requirements.